How to operate a drone? This seemingly simple question opens a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to intricate, complex flight maneuvers. Mastering drone operation requires a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical skill, encompassing pre-flight checks, navigation techniques, and a deep understanding of safety protocols. This guide will equip you with the essential tools and knowledge to confidently take to the skies.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is available online; for example, check out this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone to gain a solid foundation. From there, practice and experience will refine your skills, allowing you to confidently navigate the complexities of drone operation.
We’ll cover everything from basic pre-flight procedures and control mechanisms to advanced flight techniques and legal considerations. Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to refine your skills, this comprehensive guide will provide a structured learning path, ensuring a safe and enjoyable drone flying experience.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight inspection is crucial for ensuring safe and successful drone operation. This involves checking various components and verifying system functionality to mitigate potential risks. Neglecting this step can lead to accidents, equipment damage, and legal issues.
Pre-Flight Inspection Steps
- Battery Check: Verify battery charge level using the drone’s indicator or app. Ensure the battery is securely connected.
- Propeller Check: Inspect propellers for any damage, cracks, or imbalance. Replace damaged propellers immediately.
- GPS Signal Strength Verification: Check the GPS signal strength on your drone’s controller or app. Ensure a strong signal before takeoff (at least 8 satellites).
- Gimbal and Camera Check: Verify the gimbal moves freely and the camera is functioning correctly. Check for any obstructions.
- Visual Inspection: Conduct a visual inspection of the entire drone for any visible damage, loose parts, or debris.
- Calibration: Calibrate the compass and IMU sensors according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Environmental Check: Assess wind conditions and nearby obstacles. Avoid flying in high winds or near tall structures.
Pre-Flight Checklist Table
| Item to Check | Procedure | Acceptable Result | Unacceptable Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery Charge | Check battery level indicator | Above 80% charge | Below 20% charge |
| Propellers | Visual inspection for damage | No cracks or damage | Cracks, bends, or missing pieces |
| GPS Signal | Check GPS indicator | 6+ Satellites with strong signal | Weak signal or fewer than 6 satellites |
| Gimbal | Manually move gimbal; check camera view | Smooth movement, clear camera view | Jerky movement, obstructed camera view |
Emergency Procedures, How to operate a drone
Knowing how to react in emergency situations is critical. Loss of signal or malfunction can occur, requiring immediate action to minimize damage and ensure safety.
- Loss of Signal: If you lose signal, the drone should automatically return to its home point (if enabled). If not, immediately attempt to regain signal. If unsuccessful, visually locate the drone and attempt a manual landing.
- Malfunction: In case of a motor malfunction or other system failure, attempt to land the drone safely in a clear area. If an immediate landing isn’t possible, prioritize lowering the altitude to minimize potential damage.
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Effective drone operation hinges on understanding its controls and navigation systems. Different drones utilize various control methods, and grasping their nuances is key to safe and precise flight.
Drone Control Types and Functionalities
Most drones use either a joystick controller or a touchscreen interface. Joystick controllers offer precise manual control over the drone’s movements, while touchscreen interfaces provide a more intuitive, often simplified, control experience, often with pre-programmed flight modes.
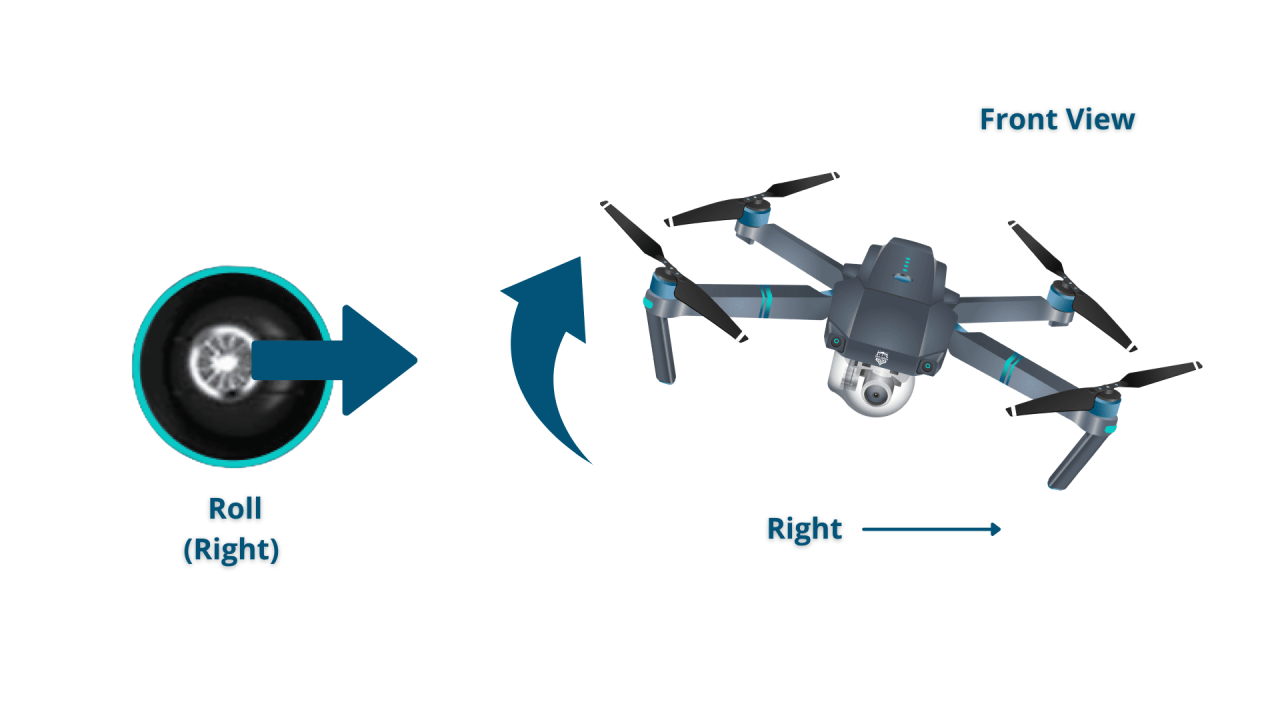
- Joystick Controllers: These typically feature two joysticks – one for controlling yaw (rotation) and throttle (altitude), and the other for controlling pitch (forward/backward) and roll (left/right). Many also include buttons for camera control and flight mode selection.
- Touchscreen Interfaces: Mobile apps provide an alternative interface, often simpler for beginners. They offer virtual joysticks or on-screen buttons for controlling the drone’s movement, camera, and flight modes.
Drone Navigation Principles

Understanding altitude hold, GPS positioning, and waypoint navigation is fundamental for precise drone control. These features significantly enhance flight stability and precision.
Successfully operating a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource to get started is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. This will equip you with the knowledge needed for safe and responsible drone operation, ensuring both your safety and the safety of those around you.
- Altitude Hold: This feature maintains a constant altitude, freeing the pilot to focus on other aspects of flight.
- GPS Positioning: GPS allows the drone to pinpoint its location and return to its home point if signal is lost (Return-to-Home or RTH function).
- Waypoint Navigation: This feature allows you to pre-program a flight path, with the drone automatically navigating to designated points.
Flight Modes Comparison
Different flight modes cater to various skill levels and flight situations. Beginner mode limits speed and responsiveness, while sport mode offers increased maneuverability and speed, and manual mode gives the pilot full control.
| Flight Mode | Description |
|---|---|
| Beginner Mode | Limited speed and responsiveness; ideal for beginners. |
| Sport Mode | Increased speed and responsiveness; for experienced pilots. |
| Manual Mode | Full manual control; requires significant skill and experience. |
Drone Compass and Sensor Calibration
- Power On: Power on the drone and controller, ensuring a strong GPS signal.
- Level Surface: Place the drone on a level, unobstructed surface.
- Calibration Procedure: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for compass and IMU sensor calibration. This usually involves rotating the drone slowly in a figure-eight pattern or following on-screen prompts in the app.
- Verification: After calibration, verify the readings in the drone’s app or control interface to ensure accuracy.
Taking Off, Flying, and Landing
Safe takeoff, flight, and landing procedures are crucial for preventing accidents and damage. Smooth maneuvers are essential, especially in windy conditions or confined spaces.
Safe Takeoff and Landing Procedures
- Pre-Flight Checks: Complete all pre-flight checks before attempting takeoff.
- Level Surface: Ensure the drone is on a level, stable surface.
- Takeoff: Gently lift the drone using the throttle control. Avoid abrupt movements.
- Stable Flight: Maintain stable flight by making smooth adjustments to the controls.
- Landing: Gradually lower the drone to the ground using the throttle control. Avoid a sudden drop.
- Power Off: Power off the drone after landing.
Maintaining Stable Flight
Maintaining stable flight, particularly in windy conditions, requires practice and skill. Understanding how wind affects the drone and adjusting accordingly is vital.
- Wind Compensation: Adjust the controls to compensate for wind gusts. Fly into the wind for stability during takeoff and landing.
- Smooth Controls: Avoid jerky movements, which can destabilize the drone.
- Altitude Adjustment: Adjust altitude to avoid strong wind gusts.
Controlling Speed, Direction, and Altitude
Effective control of speed, direction, and altitude is achieved through precise manipulation of the drone’s controls.
- Speed: Controlled by the throttle stick’s position.
- Direction: Controlled by the roll and pitch sticks.
- Altitude: Controlled by the throttle stick.
Common Mistakes of Novice Drone Pilots
Avoiding common mistakes will help ensure safe and successful flights. Understanding these pitfalls can prevent costly errors.
- Ignoring Pre-Flight Checks: This can lead to equipment malfunctions or accidents.
- Flying in High Winds: This can cause loss of control and damage.
- Flying Near Obstacles: This increases the risk of collisions.
- Improper Battery Management: This can lead to unexpected power loss.
- Neglecting GPS Signal: This can result in loss of control or inaccurate positioning.
Drone Photography and Videography
Capturing stunning aerial photos and videos requires understanding camera settings and composition techniques. Mastering these skills elevates your drone photography to a professional level.
Camera Settings and Their Effects
Different camera settings influence image quality and style. Understanding these settings is crucial for achieving the desired aesthetic.
| Camera Setting | Description | Effect on Image | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISO | Measures light sensitivity | Higher ISO increases brightness but introduces noise | Low-light photography |
| Shutter Speed | Controls exposure time | Faster shutter speed freezes motion, slower shutter speed blurs motion | Freezing action shots vs. creating motion blur |
| Aperture | Controls depth of field | Wider aperture (lower f-stop) creates shallow depth of field, narrower aperture (higher f-stop) creates greater depth of field | Portrait vs. landscape photography |
| White Balance | Adjusts color temperature | Ensures accurate color representation | Correcting color casts under different lighting conditions |
Camera Angles and Applications
Various camera angles offer unique perspectives. Choosing the right angle enhances the storytelling potential of your aerial footage.
- Bird’s-Eye View: Provides a comprehensive overview of the scene.
- High Angle Shot: Shows the subject from above, creating a sense of scale.
- Low Angle Shot: Creates a dramatic perspective, emphasizing the subject’s size or power.
- Dutch Angle: Creates a sense of unease or disorientation.
Shot Composition for Visually Appealing Results
Effective composition is essential for creating visually compelling aerial photography and videography. Applying the rule of thirds and leading lines can greatly improve your work.
- Rule of Thirds: Divide the frame into thirds both horizontally and vertically. Place key elements along these lines or at their intersections for a more balanced and visually interesting composition.
- Leading Lines: Use natural lines in the landscape (roads, rivers, etc.) to draw the viewer’s eye towards the subject.
- Symmetry and Patterns: Look for symmetrical elements or repeating patterns to create visually pleasing compositions.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and prompt troubleshooting are essential for extending the lifespan of your drone and preventing costly repairs. Addressing issues promptly minimizes potential damage.
Common Drone Problems and Causes
Understanding common drone problems and their causes helps in proactive maintenance and effective troubleshooting.
- Battery Issues: Low battery charge, damaged battery cells, or improper charging practices.
- Motor Malfunctions: Damaged propellers, loose motor mounts, or internal motor problems.
- GPS Problems: Weak signal, interference, or GPS module malfunction.
- Gimbal Issues: Mechanical problems, software glitches, or damage.
Cleaning and Maintaining the Drone
Regular cleaning and maintenance ensure optimal performance and longevity of your drone. This includes both the drone body and its components.
- Clean the body: Use a soft cloth to wipe away dirt and debris.
- Inspect propellers: Check for damage or wear and tear.
- Clean the camera lens: Use a microfiber cloth to remove any smudges or fingerprints.
- Check for loose parts: Ensure all screws and connections are secure.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Effective troubleshooting involves systematic diagnosis and problem-solving. Knowing how to approach common problems can save time and money.
- Battery Problems: Check battery charge, replace if necessary.
- Motor Malfunctions: Inspect propellers and motor mounts, replace damaged parts.
- GPS Problems: Ensure a strong signal, recalibrate GPS.
- Gimbal Issues: Check for obstructions, recalibrate gimbal, or contact manufacturer for support.
Proper Drone Storage

Storing your drone correctly extends its lifespan and protects it from damage. A dry, cool, and safe environment is essential.
- Store in a dry place: Avoid exposure to moisture.
- Store in a cool place: Avoid extreme temperatures.
- Store in a safe place: Protect from damage or theft.
- Store batteries separately: Charge batteries to around 50% before long-term storage.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Understanding and adhering to local drone regulations is paramount. Ignoring these rules can result in fines, legal action, and even criminal charges.
Importance of Understanding Drone Regulations
Drone regulations vary by location and are constantly evolving. Staying informed is crucial for responsible drone operation.
- Registration: Register your drone with the relevant authorities (e.g., FAA in the US).
- Airspace Restrictions: Be aware of restricted airspace near airports, military bases, and other sensitive areas.
- Privacy Laws: Respect individuals’ privacy and avoid filming people without their consent.
- Flight Restrictions: Adhere to any altitude or distance restrictions.
Drone Registration Process
The drone registration process varies by location but generally involves providing information about the drone and its owner. Consult your local aviation authority for specific instructions.
Airspace Restrictions and Limitations
Airspace restrictions protect public safety and national security. Flying in restricted airspace can lead to serious consequences.
- No-fly zones: These areas are often near airports or other sensitive locations.
- Altitude restrictions: Maximum altitude limits vary by location and may be lower in populated areas.
- Visual Line of Sight (VLOS): Many regulations require maintaining visual contact with the drone at all times.
Potential Legal Consequences of Violating Drone Regulations
Violating drone regulations can lead to fines, suspension of flying privileges, and even criminal charges. The penalties can be severe, so compliance is essential.
Successfully operating a drone involves more than just understanding the controls; it’s about responsible piloting, adhering to regulations, and appreciating the potential for both creative expression and technical mastery. By mastering the fundamentals Artikeld in this guide and continually practicing safe flying techniques, you’ll unlock the full potential of your drone and embark on a rewarding journey of aerial exploration.
Remember to always prioritize safety and responsible operation above all else.
Questions Often Asked: How To Operate A Drone
What type of drone is best for beginners?
User-friendly drones with GPS stabilization and autonomous flight modes are ideal for beginners. Look for models with features like “return-to-home” and obstacle avoidance.
How long does it take to learn to fly a drone?
The learning curve varies, but with consistent practice and a structured approach, you can gain proficiency within a few weeks. Start with basic maneuvers in a safe, open area.
What are the common causes of drone crashes?
Common causes include low battery, loss of signal, pilot error (sudden movements, poor judgment), and collisions with obstacles. Always prioritize safety and fly within your skill level.
How do I obtain insurance for my drone?
Drone insurance policies are available from various providers. The coverage offered varies, so compare options and choose a plan that suits your needs and the risk level of your drone operations.